Environmental Services
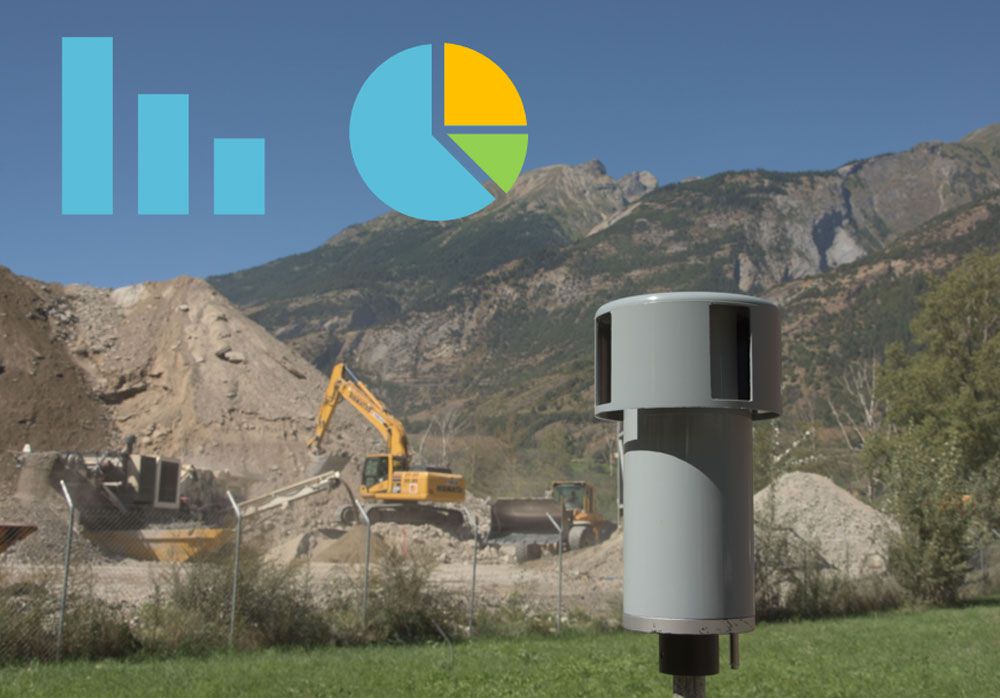

Dust monitoring
Source-differentiated dust monitoring (coarse and fine dust) and determination of dust precipitation (LRV limits) at:
- urban, industrial and rural sites
- quarries and gravel pits
- construction sites/tunnels
By means of passive (Sigma-2 and Bergerhoff) or active PM10/PM2.5 sampling.
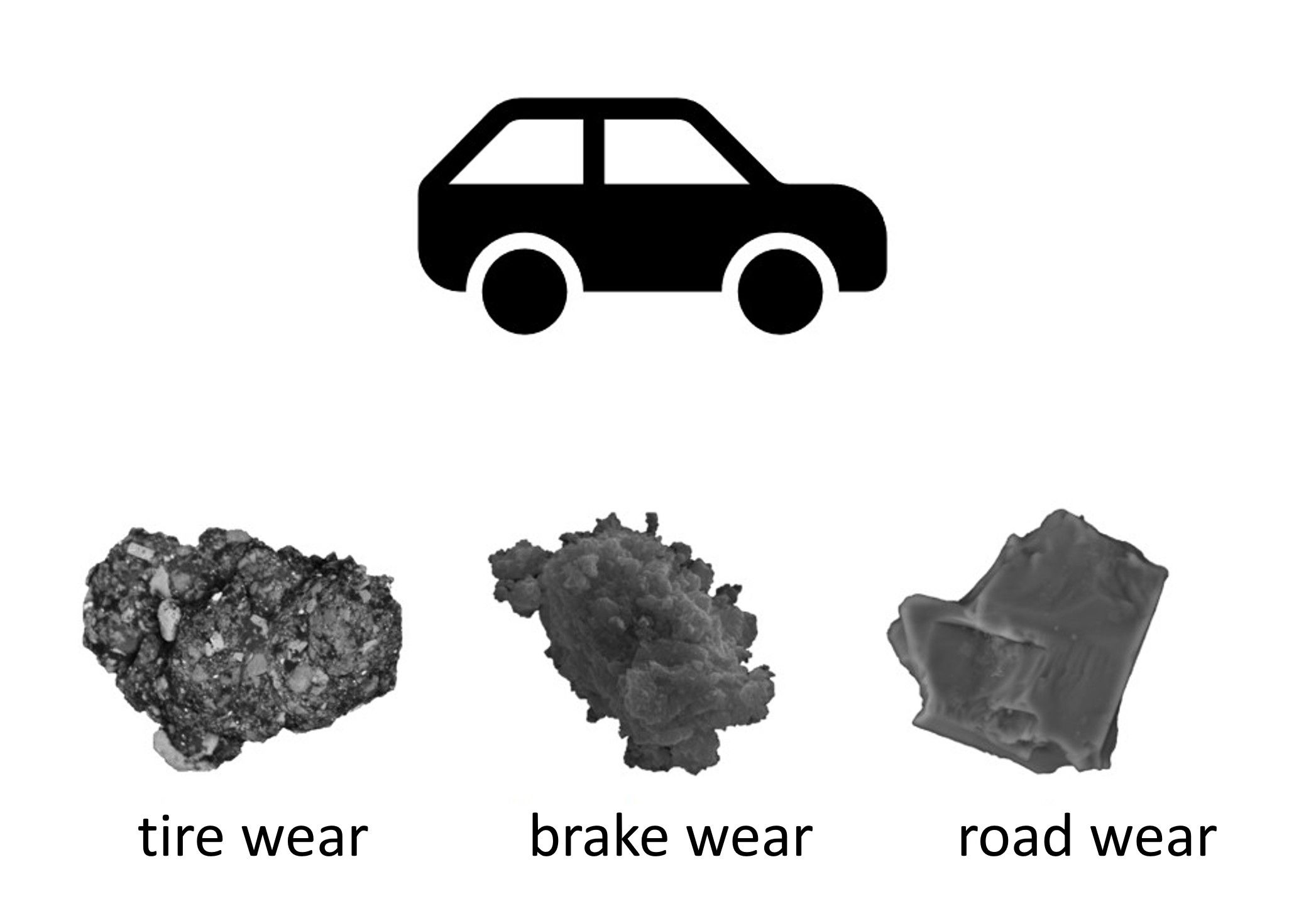

Abrasion particles from traffic
Characterization and quantification of non-exhaust particles in air and water samples:
- tire wear (microplastic, micro-rubber)
- brake wear
- road wear
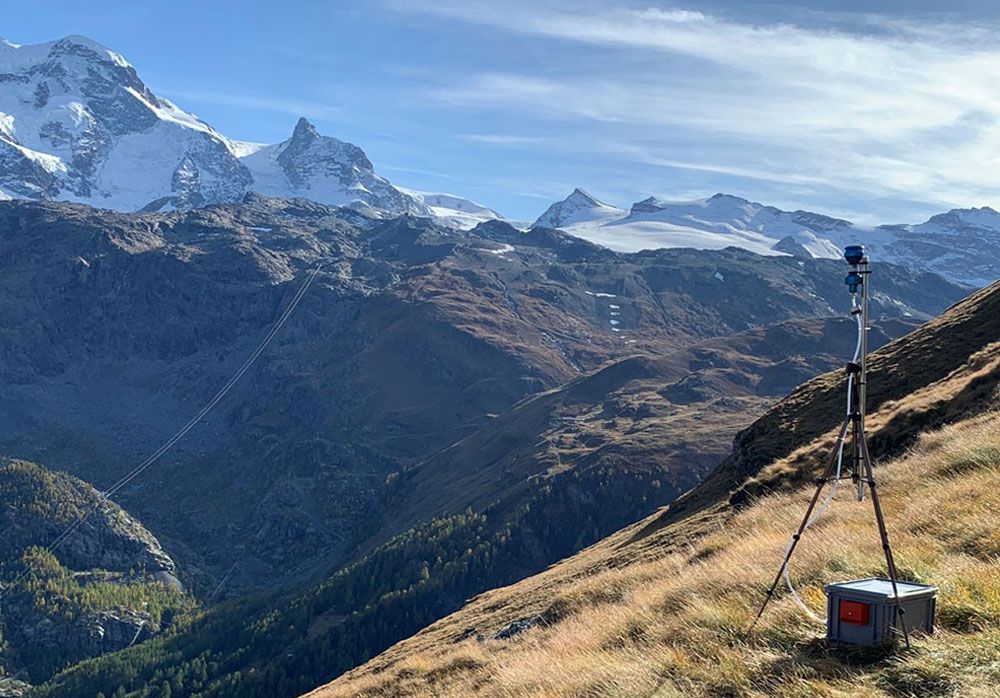

Analysis of fine dust
Active and passive measurements:
- Analysis of PM2.5 and PM10 (gravimetry)
- PM2.5 and PM10 characterization with automated SEM/EDX
- EC/OC, water soluble ions and element composition

Source apportionment of dust
Development of measurement concepts:
- who or what has caused the particle pollution?
- what is the contribution of a specific source?
- solutions for dust abatement/control
Examples:
1. Monitoring of non-exhaust abrasion particles
Yearly dust monitoring including differentiation of abrasion particles (tire wear, brake wear, road wear)
Yearly dust monitoring including differentiation of abrasion particles (tire wear, brake wear, road wear)
Source: Rausch et al., 2021 (Science of the Total Environment)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149832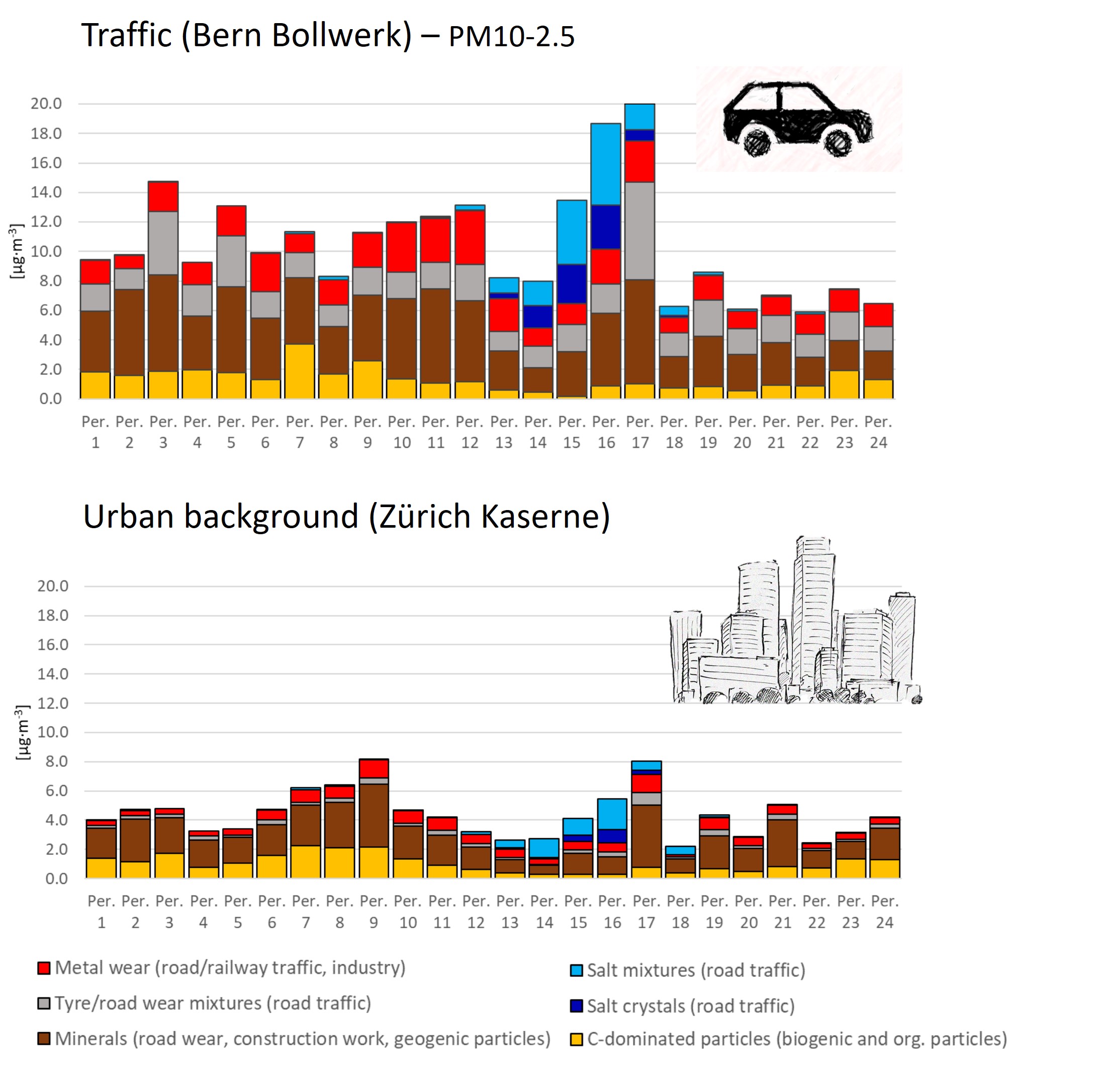
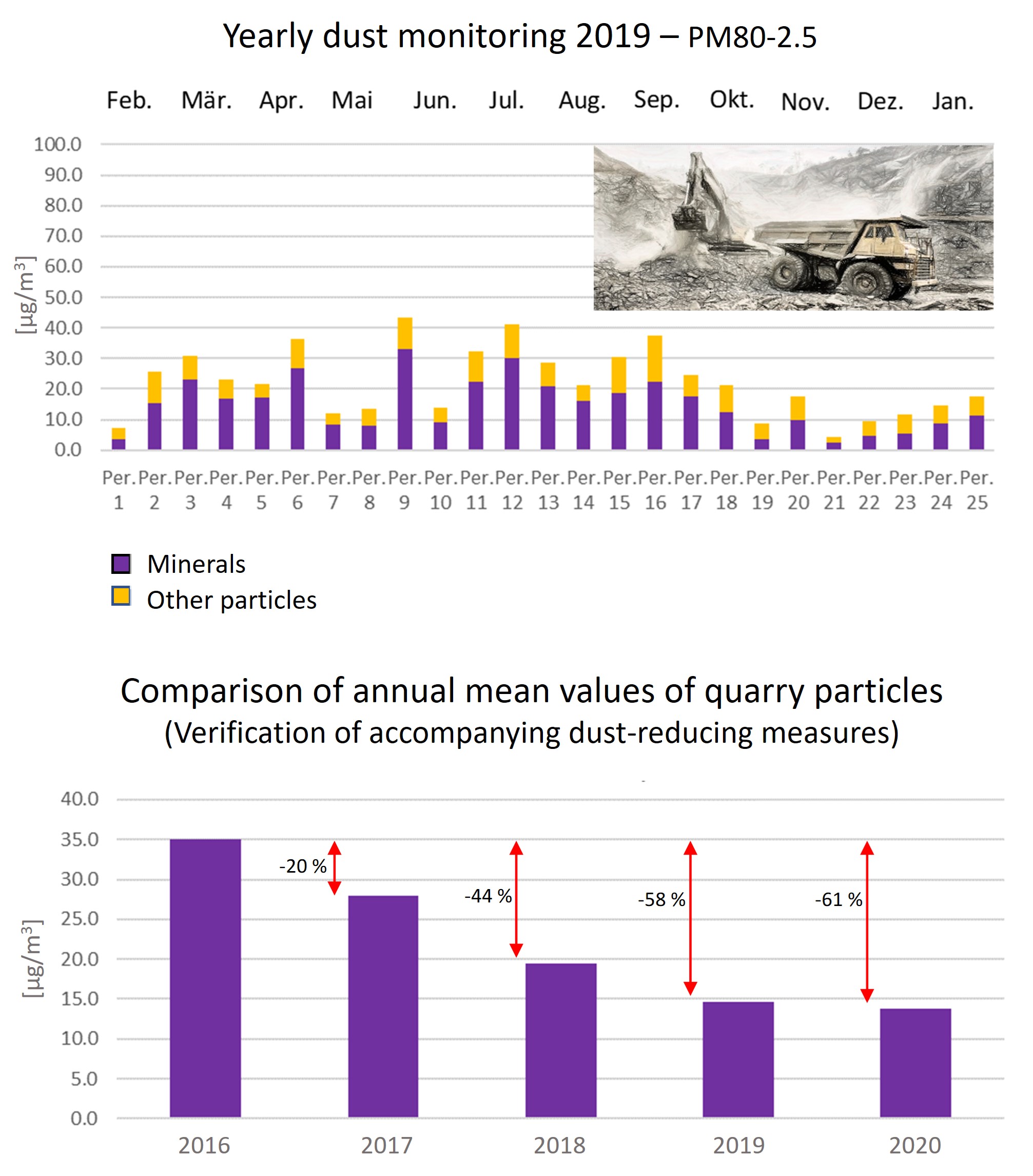
2. Dust monitoring of quarries, construction sites, recycling plants, etc.
(differentiation of a particle group)
(differentiation of a particle group)
Source: https://www.juramaterials.ch/api/rm/8R4JVM43WVA5DBP/jcf-staubmonitoring-2020-v1-0-1.pdf